Waste: fast fashion, unsustainable fabrics and cement
Waste: fast fashion, unsustainable fabrics and cement
How do you think synthetic fabrics can harm the environment?
How do you think synthetic fabrics can harm the environment?
Fabrics can be:
a. artificial or synthetic, created by people in a factory.
b. natural, these are based on what can be found in nature.
In fact, natural fabrics are much better for our health, but they are not always grown in an environmentally sustainable way. Artificial or synthetic fabrics are not good for our health or the environment. Polyester is one of the most common artificial fabrics. Polyester can be obtained by recycling five plastic bottles because the same raw material is used for their production - oil. More than 22 billion tons of polyester are produced every year. You already know everything about plastic, so you can guess that the extraction and production of oil and gas emits a lot of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It has been estimated that the fashion industry is responsible for 10 percent of climate change.
a. artificial or synthetic, created by people in a factory.
b. natural, these are based on what can be found in nature.
In fact, natural fabrics are much better for our health, but they are not always grown in an environmentally sustainable way. Artificial or synthetic fabrics are not good for our health or the environment. Polyester is one of the most common artificial fabrics. Polyester can be obtained by recycling five plastic bottles because the same raw material is used for their production - oil. More than 22 billion tons of polyester are produced every year. You already know everything about plastic, so you can guess that the extraction and production of oil and gas emits a lot of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It has been estimated that the fashion industry is responsible for 10 percent of climate change.
Ուզում եմ կարդալ ավելին

Fabrics can be:
a. artificial or synthetic, created by people in a factory.
b. natural, these are based on what can be found in nature.
In fact, natural fabrics are much better for our health, but they are not always grown in an environmentally sustainable way. Artificial or synthetic fabrics are not good for our health or the environment. Polyester is one of the most common artificial fabrics. Polyester can be obtained by recycling five plastic bottles because the same raw material is used for their production - oil. More than 22 billion tons of polyester are produced every year. You already know everything about plastic, so you can guess that the extraction and production of oil and gas emits a lot of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It has been estimated that the fashion industry is responsible for 10 percent of climate change.
a. artificial or synthetic, created by people in a factory.
b. natural, these are based on what can be found in nature.
In fact, natural fabrics are much better for our health, but they are not always grown in an environmentally sustainable way. Artificial or synthetic fabrics are not good for our health or the environment. Polyester is one of the most common artificial fabrics. Polyester can be obtained by recycling five plastic bottles because the same raw material is used for their production - oil. More than 22 billion tons of polyester are produced every year. You already know everything about plastic, so you can guess that the extraction and production of oil and gas emits a lot of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It has been estimated that the fashion industry is responsible for 10 percent of climate change.
Ուզում եմ կարդալ ավելին

Factories use the same synthetic polymers used to produce plastic to produce synthetic fabrics. In the same way, they take the monomer wagons and combine them in new polymer trains. The resulting material is stretched into threads, cooled, cut into small pieces and remelted into threads until it becomes thin plastic spaghetti. Then they get thread from them with machines and sew fabric.
Synthetic fabrics do not decompose in nature, and when they are washed, microfibers are separated from them. They pass through the filters very easily. With every wash, many very small plastic fibers end up in rivers and oceans.
Synthetic fabrics do not decompose in nature, and when they are washed, microfibers are separated from them. They pass through the filters very easily. With every wash, many very small plastic fibers end up in rivers and oceans.
Unlike large waste, the spread of these tiny microfibers is much more difficult to control. Researchers at the University of Plymouth have calculated that washing 6kg of synthetic clothing can release 700,000 microfibres.
People often forget that chemicals can enter our bodies not only from food but also from the skin. Skin is our largest organ. It absorbs everything it comes in contact with. It has been proven that polyester and other synthetic fabrics can cause an allergic reaction to the skin. Acrylic fabrics, for example (another synthetic fabric that retains heat very well and can replace wool), contain Acrylonitrile, a carcinogen that can affect our organism because it gets there through the skin and breathing.
People often forget that chemicals can enter our bodies not only from food but also from the skin. Skin is our largest organ. It absorbs everything it comes in contact with. It has been proven that polyester and other synthetic fabrics can cause an allergic reaction to the skin. Acrylic fabrics, for example (another synthetic fabric that retains heat very well and can replace wool), contain Acrylonitrile, a carcinogen that can affect our organism because it gets there through the skin and breathing.
1
2
Factories use the same synthetic polymers used to produce plastic to produce synthetic fabrics. In the same way, they take the monomer wagons and combine them in new polymer trains. The resulting material is stretched into threads, cooled, cut into small pieces and remelted into threads until it becomes thin plastic spaghetti. Then they get thread from them with machines and sew fabric.
Synthetic fabrics do not decompose in nature, and when they are washed, microfibers are separated from them. They pass through the filters very easily. With every wash, many very small plastic fibers end up in rivers and oceans.
Synthetic fabrics do not decompose in nature, and when they are washed, microfibers are separated from them. They pass through the filters very easily. With every wash, many very small plastic fibers end up in rivers and oceans.
Unlike large waste, the spread of these tiny microfibers is much more difficult to control. Researchers at the University of Plymouth have calculated that washing 6kg of synthetic clothing can release 700,000 microfibres.
People often forget that chemicals can enter our bodies not only from food but also from the skin. Skin is our largest organ. It absorbs everything it comes in contact with. It has been proven that polyester and other synthetic fabrics can cause an allergic reaction to the skin. Acrylic fabrics, for example (another synthetic fabric that retains heat very well and can replace wool), contain Acrylonitrile, a carcinogen that can affect our organism because it gets there through the skin and breathing.
People often forget that chemicals can enter our bodies not only from food but also from the skin. Skin is our largest organ. It absorbs everything it comes in contact with. It has been proven that polyester and other synthetic fabrics can cause an allergic reaction to the skin. Acrylic fabrics, for example (another synthetic fabric that retains heat very well and can replace wool), contain Acrylonitrile, a carcinogen that can affect our organism because it gets there through the skin and breathing.
1
2

The making of synthetic fabrics

The making of synthetic fabrics
Making polyester in the factory
Making polyester in the factory
A few tips:
1. If possible, avoid buying clothes made of synthetic fabrics, primarily polyester, acrylic, viscose and nylon.
2. It is not worth buying clothes made of non-wrinkly and pre-shrunk fabrics.
3. Things with natural colors are more preferable.
4. It pays to look carefully at labels, especially when buying baby or travel clothes.
5. It is better to wash the new things before wearing it.
6. If the outerwear is made of synthetic fabric, the lining should be natural.
1. If possible, avoid buying clothes made of synthetic fabrics, primarily polyester, acrylic, viscose and nylon.
2. It is not worth buying clothes made of non-wrinkly and pre-shrunk fabrics.
3. Things with natural colors are more preferable.
4. It pays to look carefully at labels, especially when buying baby or travel clothes.
5. It is better to wash the new things before wearing it.
6. If the outerwear is made of synthetic fabric, the lining should be natural.
A few tips:
1. If possible, avoid buying clothes made of synthetic fabrics, primarily polyester, acrylic, viscose and nylon.
2. It is not worth buying clothes made of non-wrinkly and pre-shrunk fabrics.
3. Things with natural colors are more preferable.
1. If possible, avoid buying clothes made of synthetic fabrics, primarily polyester, acrylic, viscose and nylon.
2. It is not worth buying clothes made of non-wrinkly and pre-shrunk fabrics.
3. Things with natural colors are more preferable.
4. It pays to look carefully at labels, especially when buying baby or travel clothes.
5. It is better to wash the new things before wearing it.
6. If the outerwear is made of synthetic fabric, the lining should be natural.
Have you heard about the Oscars? At the 92nd Academy Awards in 2020, director Elena Andreicheva and actress Léa Seydoux wore these dresses.
Elena Andreicheva's dress is handmade lyocell combined with cashmere. Léa Seydoux's dress is made from lyocell and organic silk.
Lyocell is the most ecological alternative to viscose. And viscose is a fabric that is, so to speak, between natural and artificial.
Elena Andreicheva's dress is handmade lyocell combined with cashmere. Léa Seydoux's dress is made from lyocell and organic silk.
Lyocell is the most ecological alternative to viscose. And viscose is a fabric that is, so to speak, between natural and artificial.
Viscose is obtained from natural cellulose, the main component of the tree. However, artificial chemicals are added there. First, they take the wood, grind it, and process it with a special mixture so that the cellulose dissolves and becomes a honey-like liquid. Then it is mixed with a bath of dilute acid, as a result of which the fibres of the fabric are formed. It is possible to get a similar substance without chemical additives. That's the lyocell. It was created in the USA 30 years ago.
1
2


Lyocell dress during 2020 Oscars
Elena Andreicheva (on the right)
Léa Seydoux
Have you heard about the Oscars? At the 92nd Academy Awards in 2020, director Elena Andreycheva and actress Léa Seydoux wore these dresses.
Elena Andreycheva's dress is handmade lyocell combined with cashmere. Léa Seydoux's dress is made from lyocell and organic silk.
Lyocell is the most ecological alternative to viscose. And viscose is a fabric that is, so to speak, between natural and artificial.
Elena Andreycheva's dress is handmade lyocell combined with cashmere. Léa Seydoux's dress is made from lyocell and organic silk.
Lyocell is the most ecological alternative to viscose. And viscose is a fabric that is, so to speak, between natural and artificial.
Viscose is obtained from natural cellulose, the main component of the tree. However, artificial chemicals are added there. First, they take the wood, grind it, and process it with a special mixture so that the cellulose dissolves and becomes a honey-like liquid. Then it is mixed with a bath of dilute acid, as a result of which the fibres of the fabric are formed. It is possible to get a similar substance without chemical additives. That's the lyocell. It was created in the USA 30 years ago.
1
2


Lyocell dress during 2020 Oscars
Elena Andreicheva (on the right)
Léa Seydoux

Obtaining viscose

Obtaining viscose
Fast fashion is the mass production of affordable and trendy clothes in a short period of time. What problems do you think fast fashion can create?
One of the big problems with fast fashion is that clothes, especially those made of synthetic materials, are so cheap that people are mentally prepared to buy new ones again and again. The problem is compounded by the fact that these mass-produced clothes are also of poor quality and are not suitable for long-term use. After a while, people are forced to buy new ones while wanting to keep up with fast-changing fashion trends. Social media encourage people always wear something new. Thus, we enter this cycle of consumption and cannot get out of it.
As a result, huge volumes of waste of low-quality clothes treated with various chemicals are made yearly, polluting the environment and water, harming fish and, ultimately, us humans.
Such large-scale and rapid production is also energy-intensive and contributes to abundant carbon dioxide emissions. The biggest fast fashion brands are Zara, H&M Group, UNIQLO, GAP, Forever 21, Topshop, Esprit, Primark, Fashion Nova, and New Look.
As a result, huge volumes of waste of low-quality clothes treated with various chemicals are made yearly, polluting the environment and water, harming fish and, ultimately, us humans.
Such large-scale and rapid production is also energy-intensive and contributes to abundant carbon dioxide emissions. The biggest fast fashion brands are Zara, H&M Group, UNIQLO, GAP, Forever 21, Topshop, Esprit, Primark, Fashion Nova, and New Look.
Ուզում եմ կարդալ ավելին

Fast fashion is the mass production of affordable and trendy clothes in a short period of time. What problems do you think fast fashion can create?
Ուզում եմ կարդալ ավելին

One of the big problems with fast fashion is that clothes, especially those made of synthetic materials, are so cheap that people are mentally prepared to buy new ones again and again. The problem is compounded by the fact that these mass-produced clothes are also of poor quality and are not suitable for long-term use. After a while, people are forced to buy new ones while wanting to keep up with fast-changing fashion trends. Social media encourage people always wear something new. Thus, we enter this cycle of consumption and cannot get out of it.
As a result, huge volumes of waste of low-quality clothes treated with various chemicals are made yearly, polluting the environment and water, harming fish and, ultimately, us humans.
Such large-scale and rapid production is also energy-intensive and contributes to abundant carbon dioxide emissions. The biggest fast fashion brands are Zara, H&M Group, UNIQLO, GAP, Forever 21, Topshop, Esprit, Primark, Fashion Nova, and New Look.
As a result, huge volumes of waste of low-quality clothes treated with various chemicals are made yearly, polluting the environment and water, harming fish and, ultimately, us humans.
Such large-scale and rapid production is also energy-intensive and contributes to abundant carbon dioxide emissions. The biggest fast fashion brands are Zara, H&M Group, UNIQLO, GAP, Forever 21, Topshop, Esprit, Primark, Fashion Nova, and New Look.
What did you learn how synthetic fabrics harm the environment?
What did you learn how synthetic fabrics harm the environment?
Another big source of pollution is cement. How do you think cement production harms the planet?
Another big source of pollution is cement. How do you think cement production harms the planet?
In 2012, Robert Niven, the founder of the Canadian CarbonCure organization, was a student at McGill University in Montreal. He began study the composition and production of cement in detail while writing a dissertation on the cement industry. That same year (2012), Robert attended the UN Climate Change Summit, where he saw the international demand for solutions to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. With such industry knowledge and only $10,000 left over from his student loan, Rob decided to start a company and create his own technology to reduce emissions. So he founded Carbon Cure, a company in Canada that offsets CO2 emissions from burning limestone.
1
2
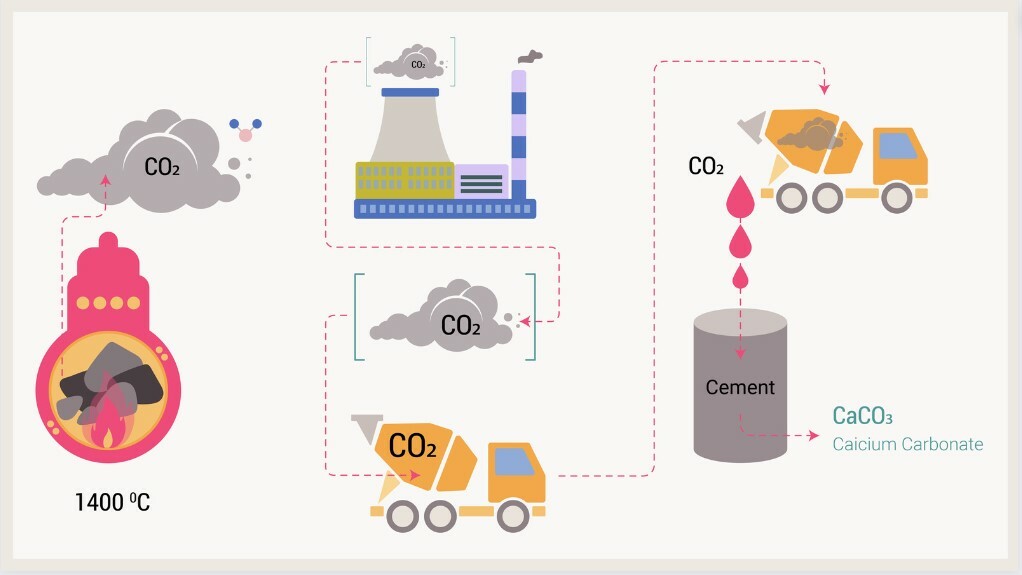
Cement is one of the most important components used in construction. It is like flour in the composition of a cake. Concrete is obtained from cement. By 2060, the world is expected to build more than 185 billion square meters of new building space. That's the equivalent of building New York every month for the next 40 years. And many of those buildings will be built using cement, a greenhouse gas source. Limestone is needed to make concrete. It is excavated from the ground, passed through a crusher, then sand and clay are added through a mill and passed through a furnace.
The raw material is heated in furnaces at a temperature above 1400°C, as a result of which the carbon contained in the rock (C) combines with oxygen (О), producing carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
The raw material is heated in furnaces at a temperature above 1400°C, as a result of which the carbon contained in the rock (C) combines with oxygen (О), producing carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
Obtaining limestone
3
Half of every 500 grams of limestone that the manufacturer puts into this furnace is released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. Thus, the cement used for making concrete accounts for up to 8% of carbon dioxide emissions in the world.
CarbonCure takes CO2 from industrial companies and adds it to the wet concrete mix. A chemical reaction begins, and the CO2 turns into calcium carbonate. The resulting concrete is more durable due to calcium carbonate. This means that during combustion, CO2 is emitted anyway, but at the expense of Carbon Cure taking their CO2 waste from industrial companies; this volume of carbon dioxide does not appear in the atmosphere but returns to the concrete.
CarbonCure takes CO2 from industrial companies and adds it to the wet concrete mix. A chemical reaction begins, and the CO2 turns into calcium carbonate. The resulting concrete is more durable due to calcium carbonate. This means that during combustion, CO2 is emitted anyway, but at the expense of Carbon Cure taking their CO2 waste from industrial companies; this volume of carbon dioxide does not appear in the atmosphere but returns to the concrete.
4
But concrete has another downside: it can have a high ammonia content. Ammonia fumes irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory organs, as well as the skin, causing lacrimation, eye pain, chemical burns of the conjunctiva and cornea, vision loss, coughing, skin redness and itching.
Concrete contains various components that can contaminate indoor air. When you have lived in a house for a long time, and you think that the building may be dangerous, you can call an expert who can take samples both from the air and from the concrete itself and give a conclusion about whether it is dangerous to live in such a building or not. And if you buy a new house, you should ask for documents on the composition of building materials, such as concrete. These data can be compared with the norms of the country.
Concrete contains various components that can contaminate indoor air. When you have lived in a house for a long time, and you think that the building may be dangerous, you can call an expert who can take samples both from the air and from the concrete itself and give a conclusion about whether it is dangerous to live in such a building or not. And if you buy a new house, you should ask for documents on the composition of building materials, such as concrete. These data can be compared with the norms of the country.

Robert Niven

In 2012, Robert Niven, the founder of the Canadian CarbonCure organization, was a student at McGill University in Montreal. He began study the composition and production of cement in detail while writing a dissertation on the cement industry. That same year (2012), Robert attended the UN Climate Change Summit, where he saw the international demand for solutions to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. With such industry knowledge and only $10,000 left over from his student loan, Rob decided to start a company and create his own technology to reduce emissions. So he founded Carbon Cure, a company in Canada that offsets CO2 emissions from burning limestone.
Cement is one of the most important components used in construction. It is like flour in the composition of a cake. Concrete is obtained from cement. By 2060, the world is expected to build more than 185 billion square meters of new building space. That's the equivalent of building New York every month for the next 40 years. And many of those buildings will be built using cement, a greenhouse gas source. Limestone is needed to make concrete. It is excavated from the ground, passed through a crusher, then sand and clay are added through a mill and passed through a furnace.
The raw material is heated in furnaces at a temperature above 1400°C, as a result of which the carbon contained in the rock (C) combines with oxygen (О), producing carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
The raw material is heated in furnaces at a temperature above 1400°C, as a result of which the carbon contained in the rock (C) combines with oxygen (О), producing carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
1
2

Կրաքարի ստացումը
Half of every 500 grams of limestone that the manufacturer puts into this furnace is released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide. Thus, the cement used for making concrete accounts for up to 8% of carbon dioxide emissions in the world.
CarbonCure takes CO2 from industrial companies and adds it to the wet concrete mix. A chemical reaction begins, and the CO2 turns into calcium carbonate. The resulting concrete is more durable due to calcium carbonate. This means that during combustion, CO2 is emitted anyway, but at the expense of Carbon Cure taking their CO2 waste from industrial companies; this volume of carbon dioxide does not appear in the atmosphere but returns to the concrete.
CarbonCure takes CO2 from industrial companies and adds it to the wet concrete mix. A chemical reaction begins, and the CO2 turns into calcium carbonate. The resulting concrete is more durable due to calcium carbonate. This means that during combustion, CO2 is emitted anyway, but at the expense of Carbon Cure taking their CO2 waste from industrial companies; this volume of carbon dioxide does not appear in the atmosphere but returns to the concrete.
3
But concrete has another downside: it can have a high ammonia content. Ammonia fumes irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory organs, as well as the skin, causing lacrimation, eye pain, chemical burns of the conjunctiva and cornea, vision loss, coughing, skin redness and itching.
Concrete contains various components that can contaminate indoor air. When you have lived in a house for a long time, and you think that the building may be dangerous, you can call an expert who can take samples both from the air and from the concrete itself and give a conclusion about whether it is dangerous to live in such a building or not. And if you buy a new house, you should ask for documents on the composition of building materials, such as concrete. These data can be compared with the norms of the country.
Concrete contains various components that can contaminate indoor air. When you have lived in a house for a long time, and you think that the building may be dangerous, you can call an expert who can take samples both from the air and from the concrete itself and give a conclusion about whether it is dangerous to live in such a building or not. And if you buy a new house, you should ask for documents on the composition of building materials, such as concrete. These data can be compared with the norms of the country.
4

Robert Niven
What did you learn how cement production harms the environent?
What did you learn how cement production harms the environent?
Discussion 5: Key questions
If you want to further prepare for the discussion, below you will find the main questions of the upcoming meeting.
1. Analysing a cartoon picture on the topic of fast fashion.
2. Debate over the "Fast fashion factories should be closed".
1. Analysing a cartoon picture on the topic of fast fashion.
2. Debate over the "Fast fashion factories should be closed".
